Essential Linux Commands: A Quick Reference Guide
Linux commands are the foundation of effective system administration and everyday tasks. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, knowing these fundamental commands is essential. Let us look at some key commands that will help you navigate the Linux environment with ease.
Date and Time Commands:
Display the current date and time.
dateView the calendar
Example: cal
Example: cal 5 2010 (display May 2010 calendar)File and Directory Management:
Clear the terminal screen.
clearList directories and files.
lsCreate a new user.
useradd vishalSet or change a user password.
passwd vishalCreate a user without a password.
passwd -d vishalRename a user.
usermod -l n-name o-nameAdd a user to a group.
usermod -g group userCreate a user without a duplicate directory.
useradd -n vishalDelete user with their directory.
userdel -r vishal Forcefully remove a directory.
rm -rf directoryView group memberships.
groups vishalView user directory.
vi /etc/passwdCreate a group.
groupadd salesView group directory.
vi /etc/groupRename a group.
groupmod -n n-name o-nameHow to find files in Linux :
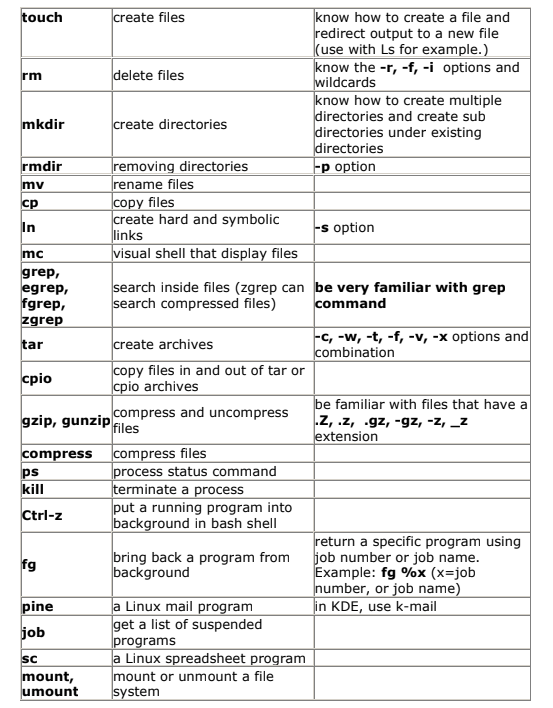
Find the file using file name in Linux.
find /home/user/Documents -name "report.txt"Find the file using it’s extension in Linux.
find /home/user/Documents -name "*.pdf"Find the file by size in linux (larger than 10 MB)
find /home/user/Documents -size +10M
System and Configuration:
Switch user.
su vishalGraphically view any configuration.
system-config-Create a new tab.
ctrl+shift-tSwitch to the next/previous tab.
ctrl+PgUp/DnView files of any command.
/usr/share/docOther Useful Commands:
View help about any calendar.
whatis calView detailed help about the date command.
date --helpView manual pages about ls.
man lsView information about history.
info historyFind the path of any directory or command.
which dirRefers to your home directory.
~ (Tilde)Time-Saving Tips:
Fully stop a command.
ctrl+c Stop the terminal.
ctrl+dSend a program into the background or temporary halt.
ctrl+zCheck programs running in the background.
jobsBring a halted program back to run.
fg 1 or 2 or 3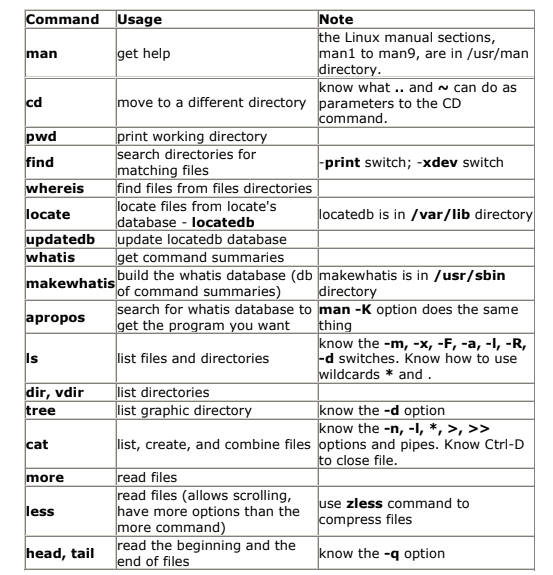
Conclusion:
These Linux commands provide a foundation for effective system management. Whether you are dealing with files, users, or configurations, mastering these commands will boost your productivity. Stay tuned for more Linux tips and tricks at Linux Guru!
