How to setup Nginx ingress using helm
Ingress-Nginx is a Ingress controller of kuberntes. An ingress is an object that allows you to access your services from outside of the cluster. Using the Nginx Ingress controller you can configure load balancing, SSL/TLS certification, URL rewrite, and many more.
In this post, I will show you How to Install and configure the Nginx ingress controller with cert-manager and HTTPS with Let’s Encrypt.
1. Install helm
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes. Helm is useful to create deployments, Automation, packaging, and configuring applications and services on Kubernetes.
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
curl https://baltocdn.com/helm/signing.asc | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https --yes
echo "deb https://baltocdn.com/helm/stable/debian/ all main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/helm-stable-debian.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install helm
helm version2. Install Nginx ingress
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm repo update
helm install nginx-ingress ingress-nginx/ingress-nginxRun the below command to get the ingress controller public IP Address and point it to the domain you have.
sudo kubectl get serviceNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.52.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 8m15s
nginx NodePort 10.52.9.44 <none> 80:31278/TCP 18s
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.52.5.136 34.134.29.156 80:31949/TCP,443:30161/TCP 3m7s
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.52.7.206 <none> 443/TCP 3m7s
3. Deploy a simple application
Deploy a simple Nginx application to test our deployment and access it using the Nginx ingress controller in the browser. We will deploy the Nginx web service in Kubernetes and expose it to the NodePort.
Deploy :
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort
Expose :
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort
4. Create Nginx ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: vishalvyas.com
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
path: /
kubectl create -f `ingress.yaml
Run this command to check the status of the ingress and URL/IP.
kubectl get ing
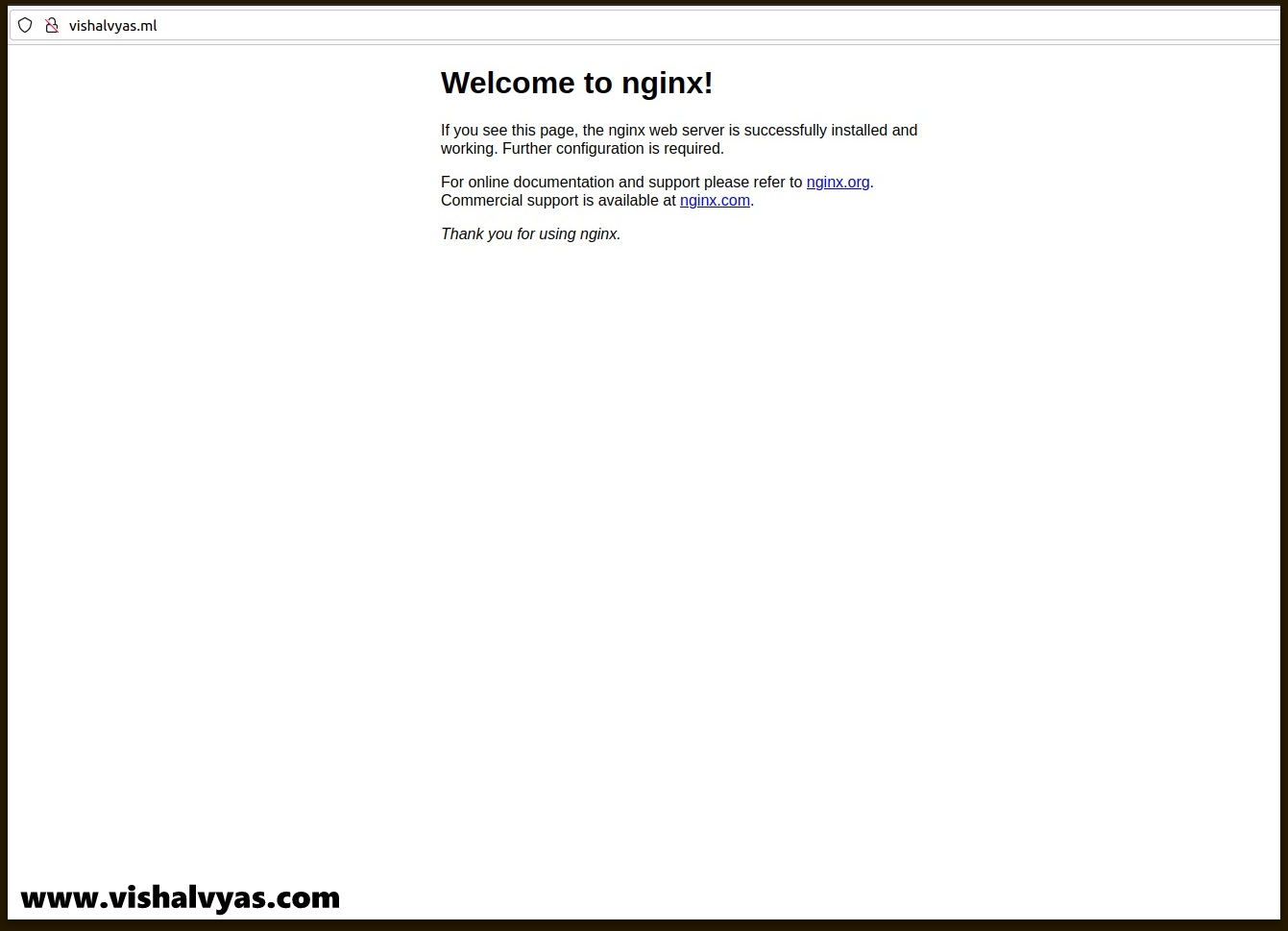
Copy the URL/IP and open it in the browser.
You can see that Nginx web page that mean ingress working successfully, But you can see that it’s not secure, So we have to setup HTTPS SSL certificate for that.
Install Cert manager
Cert manager issues certificates and certificate issuer for Kubernetes clusters. Let’s deploy cert-manager on our Kubernetes cluster.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.8.0/cert-manager.yaml
Configure a Let’s Encrypt Issuer
There is a rate limit on the Let’s Encrypt production issuer. We will start with the Let’s Encrypt staging issuer first and then will move to the production issuer. Run the below command and Replace your email address.
kubectl create --edit -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cert-manager/website/master/content/docs/tutorials/acme/example/staging-issuer.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: user@example.com
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging
# Enable the HTTP-01 challenge provider
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
Also create production-issuer.yaml and update you Email ID.
kubectl create --edit -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cert-manager/website/master/content/docs/tutorials/acme/example/production-issuer.yamlapiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: user@example.com
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-prod
# Enable the HTTP-01 challenge provider
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
Update Nginx ingress
Lets Update let’s encrypt staging issuer in nginx ingress and TLS secret.
kubectl apply -f ingress.yamlMake sure to update the staging issuer cert-manager.io/issuer: "letsencrypt-staging"
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress
annotations:
cert-manager.io/issuer: "letsencrypt-staging"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: vishalvyas.ml
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
path: /
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- vishalvyas.ml
secretName: vishalvyas
Cert-manager will read these annotations and use them to create a certificate, which you can request and see and wait until the status True
kubectl get certificate vishalvyas
NAME READY SECRET AGE
vishalvyas True vishalvyas 32m
Update production issuer
Now it’s time to update the production cluster issuer in the ingress controller.
kubectl apply -f ingress.yamlapiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress
annotations:
cert-manager.io/issuer: "letsencrypt-prod"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: vishalvyas.ml
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80
path: /
# This section is only required if TLS is to be enabled for the Ingress
tls:
- hosts:
- vishalvyas.ml
secretName: vishalvyas
We also need to delete the existing secret which we create for staging, Cert manager will reprocess the request and update issuer.
kubectl delete secret vishalvyas
You can check the status of your certificates using this command.
kubectl describe certificate vishalvyas
You can see that certificates are successfully issued.
Normal Generated 33m cert-manager-certificates-key-manager Stored new private key in temporary Secret resource "vishalvyas-6nkfs"
Normal Requested 33m cert-manager-certificates-request-manager Created new CertificateRequest resource "vishalvyas-hpt58"
Normal Issuing 33m (x3 over 36m) cert-manager-certificates-issuing The certificate has been successfully issued
Now, let’s access a web page, It should serve us an HTTPS secure page.
Hope you like this article.



Thanks for writing wonderful article. keep continue the good work. need your support for me too. How to Install Docker on Ubuntu 20.04 Easily